Summer in Paris
Grades 9-10
Already today, there are more and more heat waves, which are a burden for people living
in cities. Older people in particular suffer, and for some it has life-threatening
consequences. Against the background of climate change and forecasts that two thirds of
the world’s population will live in cities by 2050, the urban climate is a current and
relevant topic.
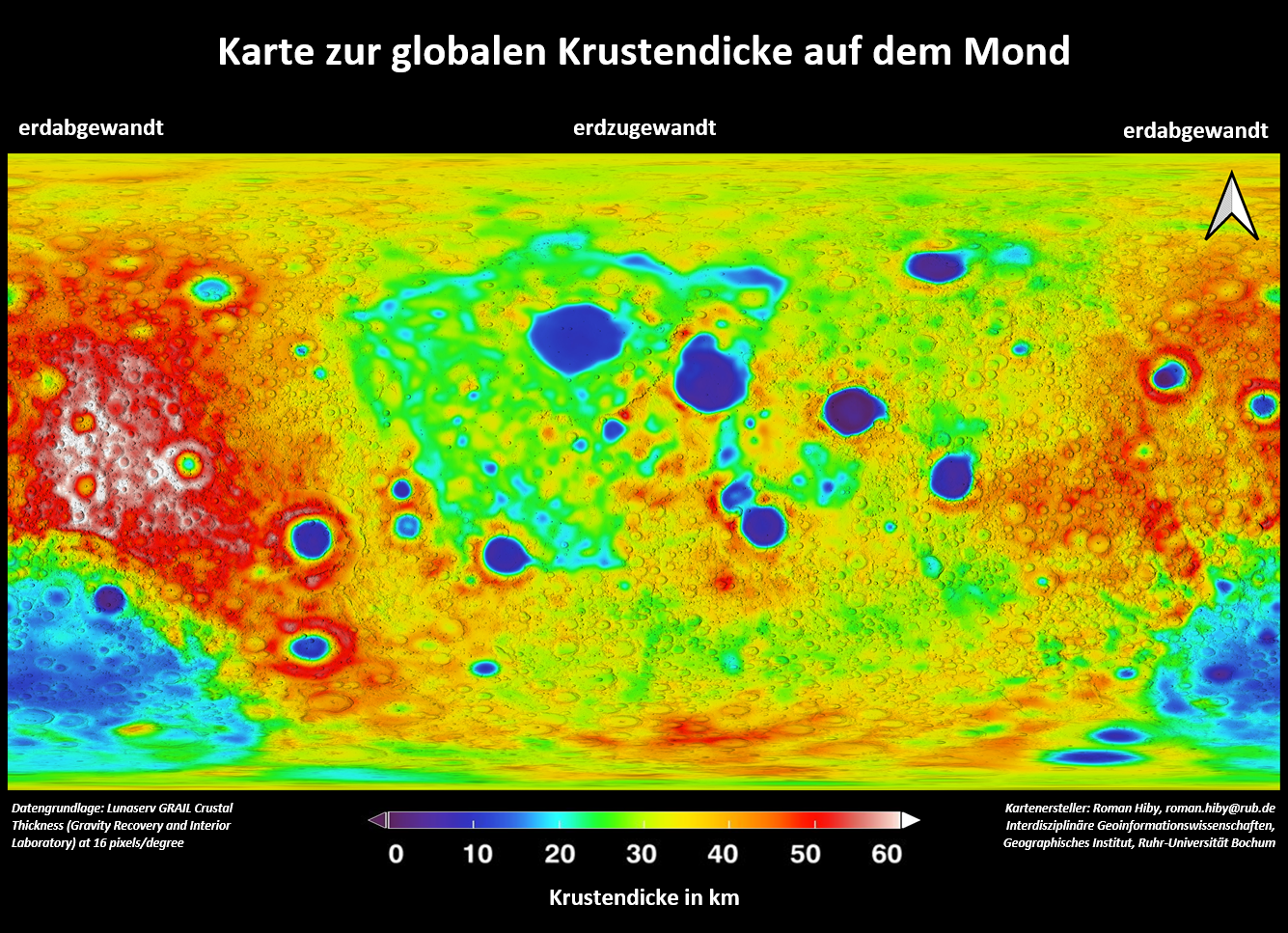
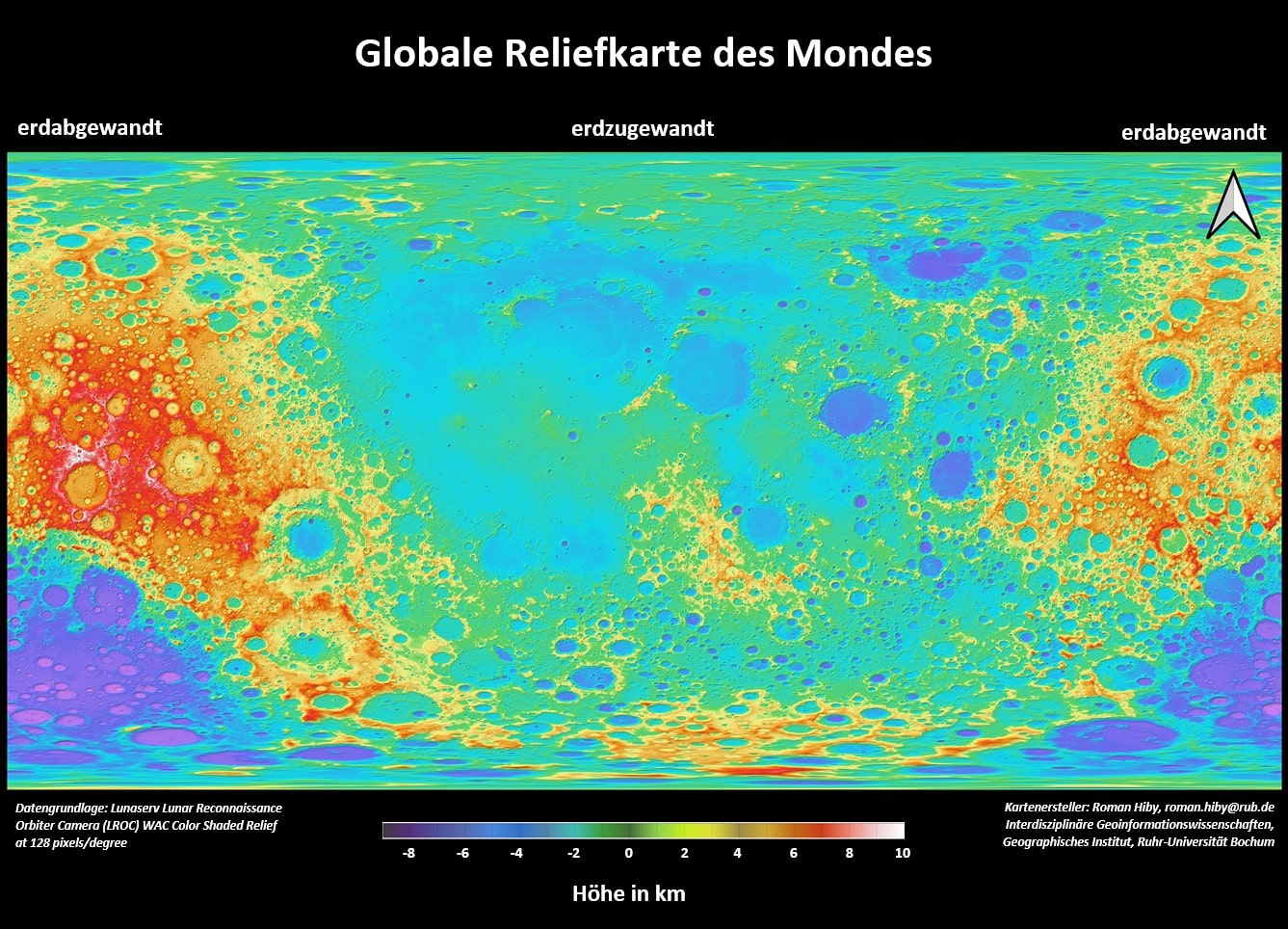
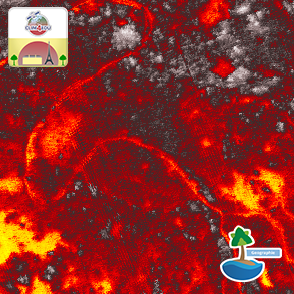
Paris is one of the most severely affected cities in Europe. Summer nights here are up to
4 K warmer than in the surrounding countryside. During the heat waves in the summer of
2022, Paris was hit particularly hard by the heat, but projects are already underway to
reduce the problem by converting traffic areas into green spaces.
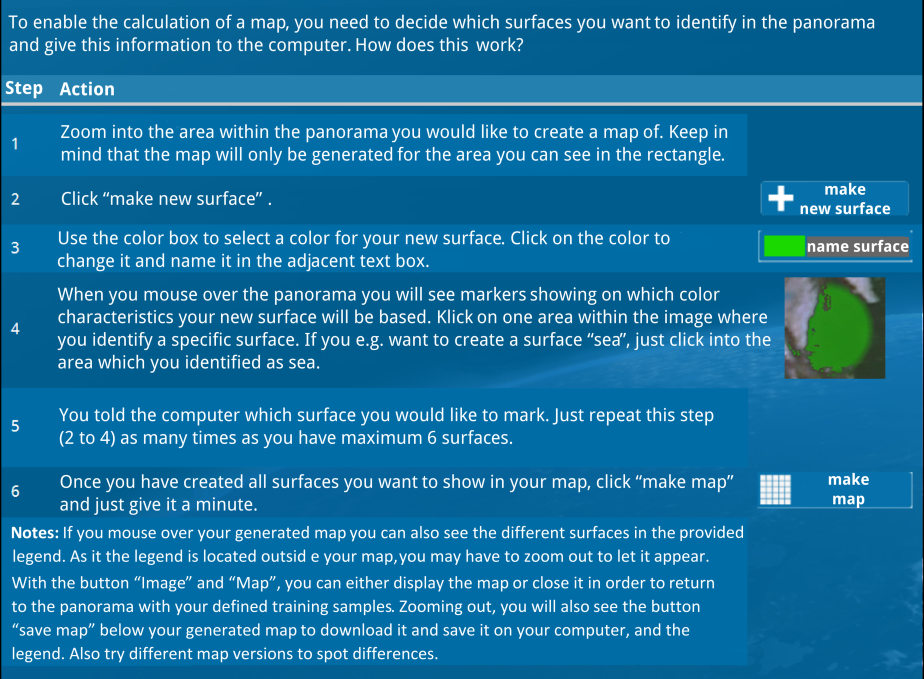
The work sheet and the app use satellite images with true colours, plant cover and
surface temperatures to take a closer look at the causes of the Urban Heat Island Paris
and, based on this, discuss planned and implemented measures against it.
App “Columbus Eye” free of charge at Google Play or in the App Store:


Part “Summer in Paris”
Objectives: The students…
- explain the concept of an Urban Heat Island and the dangers it poses,
- describe the characteristics of particularly warm/cool places,
- identify main urban planning problems in relation to Urban Heat Islands,
- explain the effects of measures to reduce the heat island effect,
- evaluate measures to reduce the heat island effect against the background of costs
and benefits for the population.
Download
working sheet